In defence of web scraping
SOURCE:
- Open internet
- Big data and web scraping
- Season 3 of westworld
- Robots_exclusion_standard
- Search_engine_scraping
- TheProject
- Internet was not predicted
- The Internet
When I mention to others that I’m working on “web scraping” for my personal project, they either don’t understand what I’m referring to or react with apprehension. The term “web scraping” carries a negative connotation these days, often being perceived as unethical or even illegal.
Why illegal?
Some companies might even take legal action against you (there have been numerous lawsuits related to web scraping over the years) or engage in lobbying efforts to outlaw it. While these efforts may not be successful, they can create a deterrent effect: individuals might feel guilty for engaging in potentially illegal activities.
Why unethical?
Naturally, if you follow the news, you might think of incidents involving Cambridge Analytica or similar organizations that scrape social media user data and manipulate public opinion through targeted advertisements and the dissemination of fake news.
Today, it is evident that web scraping can be used to sell data to governments, industries, advertising companies, or even to influence election outcomes. Such practices are undoubtedly harmful, as the ultimate goal is control and manipulation, pushing people to buy or vote for someone who has paid for their support. If the sole objective is money and power, the internet will become saturated with advertisements and surveillance.
If the goal is to have a centralized system that monitors everything and data with a single owner, you just need to choose to place all user-collected data behind an authentication system.
While these concerns are valid, it doesn’t mean that web scraping should be entirely condemned. It might be worthwhile to reevaluate this practice and explore whether its direction can be changed for the better.
To achieve this, we must first revisit the fundamentals and appreciate the incredible nature of the web itself.
What is the web?

Essentially, the web consists of interconnected documents (with hyperlinks where clicking on a link directs you to another document from a specific computer). These linked documents can be displayed by requesting a specific computer to download them to your browser using an HTTP/HTTPS protocol.

These computers are referred to as ‘servers’ because they are set up to listen for and respond to our requests. ‘Servers’ run a program in the background, awaiting incoming messages, so they can provide the requested document.
This may be a fundamental definition of what we know as the web. Its tremendous value today lies in the fact that all these documents, originating from various computers. Similar to university papers or academic books, they often include source references.
It is crucial to emphasize that there is no central super-computer overseeing all these documents. Likewise, there are no super-computers managing all the individual computers. Instead, information is distributed horizontally in a decentralized manner across various computers.
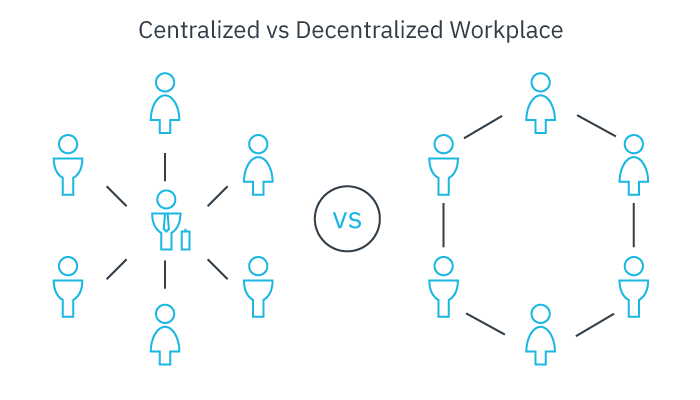
Despite the level of control exerted by institutions, companies, and states in the physical world, no single entity holds absolute authority over the online world. In fact, some argue that the web has intentionally been designed to be uncontrollable, not necessarily by the US army, but rather by each person who contributes document files to the web.
In essence, the web can be likened to an extensive library of interconnected documents with no single owner. If data had owners and strict copyright laws, it would be impossible to construct a search engine. The web would then become a disorderly library with no reliable way of locating the documents that users require.

What is web scraping now?
“The largest public known incident of a search engine being scraped happened in 2011 when Microsoft was caught scraping unknown keywords from Google for their own, rather new Bing service. But even this incident did not result in a court case.”
“One possible reason might be that search engines like Google are getting almost all their data by scraping millions of public reachable websites, also without reading and accepting those terms. A legal case won by Google against Microsoft would possibly put their whole business as risk.”
Wikipedia: Search engine scraping
Web scraping is an automated method of gathering data from the internet. When an API is unavailable, the process typically involves extracting data from a website’s HTML file, identifying the relevant information, and saving it to a database. Once the data is publicly available on the web, it can be stored, monitored, and utilized by anyone.
One of the co-founders of Google had a vision of downloading all the HTML documents on the web and creating a massive network of nodes based on the links found within each document. To accomplish this, he would need to develop a rule that identifies links within web pages, converts them into nodes, and determines their position within the network.
We can easily see here that Google is today’s most advanced web scraping company in existence. And, if we really want to access it, Google’s web scraping gives us the most amazing access to culture that there is.
No Web Scraping, no search engine
To navigate the vastness of the internet, search engines like Google are crucial. Without them, finding information and resources would be incredibly difficult, and we would be limited to only accessing content from highly influential individuals or powerful companies who have the means to promote their content.
So now where can we go?
Today, many of us still underestimate the full potential of web scraping, perhaps because it is not an easy technique to master. Typically, we tend to associate web scraping with finding cheap deals on flights, restaurants, and products, which is certainly useful. However, there may be other, even more valuable applications for web scraping.
In particular, the web is uniquely suited to handle big data, which is essential for machine learning. Without the web, there would be no big data, and without big data, machine learning would be impossible. With the increasing power of computers, we now have access to machine learning techniques that can scrape the web, classify and process vast amounts of data, and extract meaningful insights. This opens up many exciting possibilities, including:
- AI can help doctors diagnose diseases more accurately and quickly by analyzing medical images, symptoms, and patient history
- AI can help predict and mitigate the effects of climate change by analyzing data from weather sensors, satellite imagery, and other sources
- AI can help emergency responders better respond to natural disasters by analyzing data from sensors, social media, and other sources
- AI can detect fraudulent activity in financial transactions and prevent it from happening in the first place
- AI can help monitor and protect the environment by analyzing data on pollution, deforestation, and other factors
- AI can be used to optimize energy usage and reduce carbon emissions in industries like transportation, manufacturing, and agriculture
- automatized customer services that use advanced chatbots to problem-solve help you mend stuff (by sending photos to them) and find what you need to buy for you
- AI can help people with disabilities by improving accessibility, creating custom devices and technologies
- machine learning can give us very precise statistics in economy, urbanism, criminality …
- AI can help farmers optimize their crops and reduce waste by providing insights into soil quality, weather patterns, and crop health
- AI can assist scientists in analyzing vast amounts of data, modeling complex systems and predicting outcomes, and facilitating collaborations across research communities
- AI can automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and provide data-driven insights to help employees work more efficiently
- AI could be used to manage and optimize decentralized renewable energy grids. This could involve predicting energy supply and demand, managing energy storage systems, and balancing energy usage across a network of decentralized generators and consumers
-
…
Other suggestions?
In summary, Web scraping can give us better access to culture, science, and with better access to culture, science… humans can maybe act in the world with greater attention to important things and/or awareness.